728x90
728x90

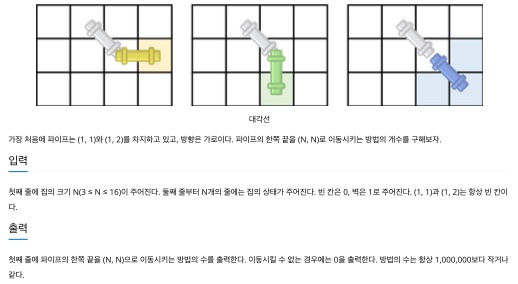
쉬운듯 쉽진 않았던 문제다.
<틀린코드>
더보기
더보기
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int result = 0;
static int[][] room;
static Queue<Pipe> pipe = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
room = new int[N+1][N+1];
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j=1; j<N+1; j++) {
room[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
br.close();
pipe.add(new Pipe(1, 1, 1, 1, 2));
cal();
System.out.print(result);
}
public static void cal() {
while(!pipe.isEmpty()) {
Pipe temp = pipe.poll();
int tempC = temp.twoC;
int tempR = temp.twoR;
if(tempC==N && tempR==N) {
result = result + 1;
continue;
}
switch(temp.type) {
case 1:
if(tempR<N && room[tempC][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(1, tempC, tempR, tempC, tempR+1));
if(tempC<N && room[tempC+1][tempR]==0 && room[tempC+1][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(3, tempC, tempR, tempC+1, tempR+1));
}
}
break;
case 2:
if(tempC<N && room[tempC+1][tempR]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(2, tempC, tempR, tempC+1, tempR));
if(tempR<N && room[tempC][tempR+1]==0 && room[tempC+1][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(3, tempC, tempR, tempC+1, tempR+1));
}
}
break;
case 3:
boolean can = true;
if(tempR<N && room[tempC][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(1, tempC, tempR, tempC, tempR+1));
}else {
can = false;
}
if(tempC<N && room[tempC+1][tempR]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(2, tempC, tempR, tempC+1, tempR));
}else {
can = false;
}
if(can==true && room[tempC+1][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(3, tempC, tempR, tempC+1, tempR+1));
}
}
}
}
}
class Pipe{
int type; //가로:1 세로:2 대각선:3
int oneC, oneR;
int twoC, twoR; //두 칸의 파이프 중 보다 오른쪽||밑 에 있는 파이프를 뜻함
Pipe(int type, int oneC, int oneR, int twoC, int twoR){
this.type = type;
this.oneC = oneC;
this.oneR = oneR;
this.twoC = twoC;
this.twoR = twoR;
}
}
나름 혼자 술술 풀었고 예제도 모두 풀어내길래 기대했다.
심지어 정답 퍼센테이지도 곧잘 올라 잠깐의 일장춘몽을... 후..
늘 발목을 붙잡는 시간초과.
항상 문제를 풀어보면 정확도엔 큰 미스가 없지만 시간초과가 제동을 걸곤 한다.
추릴대로 추려도 여전히 시간초과가 나길래 질문들을 뒤져봤다.
Queue 대신 ArrayList를 사용하면 해결된단 말이 있길래 마음이 심란해졌다.
다른 코드들을 보니 내 코드랑 좀 달라 역시 갈아엎어야 하나 고민하던 찰나였고, 반복되는 시간초과에 질리던 참이었다.
설마하고 적용해봤더니 통과됐다..
이번엔 기분이 좋으면서도 마냥 좋진 않았다.
형식의 디테일을 계산하지 못한 미흡함이 원인이었겠지만
혹여 나중에 중요한 시험에서 이런 일이 일어난다면 좀 슬플 것 같더라.
이번 문제에선 내 코드가 마음에 들어서.. 다른 코드도 참고하지 않았고 약간만 수정하고 싶었는데 이런 식의 수정은...ㅠㅠ
LinkedList와 ArrayList 차이에 대해 알고 있지만 다시 더 정확히 파악해야겠다.
그리고, 그래도 다른 사람 코드 길이에 비해 긴편이라 참고해 공부해야겠다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int result = 0;
static int[][] room;
static ArrayList<Pipe> pipe = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
room = new int[N+1][N+1];
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j=1; j<N+1; j++) {
room[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
br.close();
pipe.add(new Pipe(1, 1, 2));
cal();
System.out.print(result);
}
public static void cal() {
while(!pipe.isEmpty()) {
Pipe temp = pipe.remove(pipe.size()-1);
int tempC = temp.twoC;
int tempR = temp.twoR;
if(tempC==N && tempR==N) {
result = result + 1;
continue;
}
switch(temp.type) {
case 1:
if(tempR<N && room[tempC][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(1, tempC, tempR+1));
if(tempC<N && room[tempC+1][tempR]==0 && room[tempC+1][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(3, tempC+1, tempR+1));
}
}
break;
case 2:
if(tempC<N && room[tempC+1][tempR]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(2, tempC+1, tempR));
if(tempR<N && room[tempC][tempR+1]==0 && room[tempC+1][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(3, tempC+1, tempR+1));
}
}
break;
case 3:
boolean can = true;
if(tempR<N && room[tempC][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(1, tempC, tempR+1));
}else {
can = false;
}
if(tempC<N && room[tempC+1][tempR]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(2, tempC+1, tempR));
}else {
can = false;
}
if(can==true && room[tempC+1][tempR+1]==0) {
pipe.add(new Pipe(3, tempC+1, tempR+1));
}
}
}
}
}
class Pipe{
int type; //가로:1 세로:2 대각선:3
int oneC, oneR; //one이 아닌 two를 사용할 것을 의미함
int twoC, twoR; //두 칸의 파이프 중 보다 오른쪽||밑 에 있는 파이프를 뜻함
Pipe(int type, int twoC, int twoR){
this.type = type;
this.twoC = twoC;
this.twoR = twoR;
}
}
728x90
728x90
'[Java]BaekJoon.AC' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java]백준 BaekJoon.AC 1967 : 트리의 지름 (dfs, Tree) (0) | 2022.01.09 |
|---|---|
| [Java]백준 BaekJoon.AC 1504 : 특정한 최단 경로 (다익스트라, ArrayList) (0) | 2021.12.10 |
| [Java]백준 BaekJoon.AC 16236 : 아기 상어 (Queue, bfs) (0) | 2021.12.08 |
| [Java]백준 BaekJoon.AC 1043 : 거짓말 (ArrayList) (0) | 2021.12.07 |
| [Java]백준 BaekJoon.AC 15686 : 치킨 배달 (브루트포스, Dot) (0) | 2021.12.03 |
| [Java]백준 BaekJoon.AC 14502 : 연구소 (너비우선탐색-bfs, 브루트포스 알고리즘) (0) | 2021.11.29 |
| [Java]백준 BaekJoon.AC 13549 : 숨바꼭질3 (너비우선탐색-bfs, Queue) (0) | 2021.11.24 |
| [Java]백준 BaekJoon.AC 12865 : 평범한 배낭 (다이나믹 프로그래밍, knapsack) (0) | 2021.11.18 |